Introduction to Haptic Feedback in VR
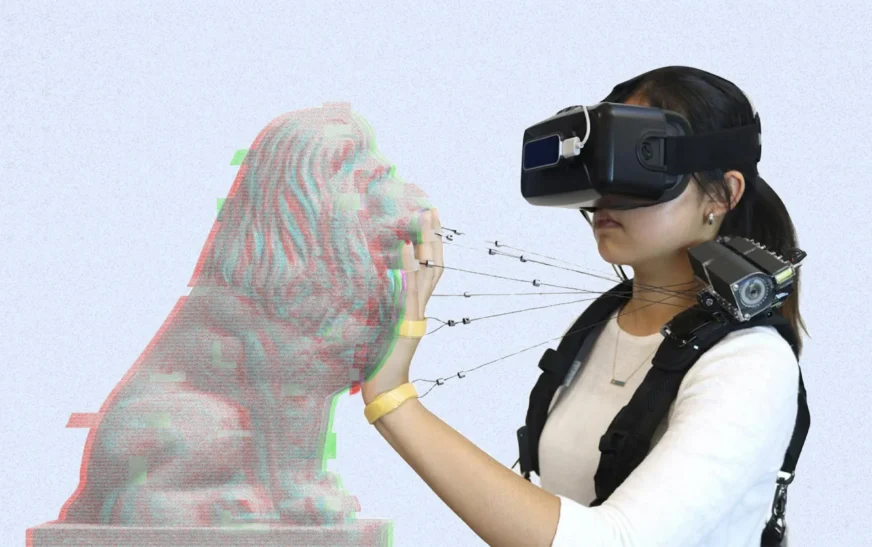
Imagine stepping into a virtual world that feels as real as your own. You reach out to touch a rock, and instead of just seeing it, you can actually feel its rough surface beneath your fingers. This immersive experience is made possible by haptic feedback in VR—a technology that’s transforming the way we interact with virtual environments. Gone are the days when visual and auditory cues were enough to create an engaging experience. Now, with the addition of realistic touch sensations, users can fully engage their senses.
Haptic feedback is not just about feeling; it’s about enhancing interaction in ways we’ve never imagined before. As this technology advances, so too does our ability to connect with digital worlds on a deeper level than ever before. In this blog post, we’ll explore the various types of haptic feedback available today and how they work to enrich our experiences in VR settings. Get ready to dive into a realm where every touch adds another layer of realism!

Types of Haptic Feedback and How They Work
Haptic feedback comes in various forms, each designed to enhance the virtual experience. One common type is vibrotactile feedback, which uses small motors to create vibrations. This simulates sensations like a heartbeat or footsteps.
Another form is force feedback, often found in gaming controllers and simulation devices. It resists movement to mimic real-world forces, making interactions feel more authentic.
Ultrasonic haptics takes it a step further by using sound waves to create tactile sensations without physical contact. Users can “feel” textures and shapes as if they were touching them directly.
Electrostatic technology generates tiny electrical charges on touch surfaces. This allows users to feel different textures while interacting with virtual objects.
Each of these types contributes uniquely to creating immersive environments that elevate user interaction and engagement within VR experiences.
Benefits of Haptic Feedback in VR
Haptic feedback in VR transforms the way users interact with virtual environments. It bridges the gap between sight and touch, creating a more immersive experience.
Users can feel textures, vibrations, and impacts that mimic real-world sensations. This realistic interaction enhances emotional engagement within the virtual space.
For developers, incorporating haptic technology can elevate game design and storytelling. It allows for nuanced player responses to in-game events. A simple action can become thrilling when accompanied by tactile feedback.
Moreover, haptic systems cater to various applications beyond gaming—training simulations benefit immensely from this technology. Users gain practical skills through realistic practices without real-world consequences.
Accessibility also improves with haptic feedback; it provides alternative cues for those who may struggle with visual or auditory information. Enhanced interaction fosters inclusivity in virtual experiences, making them richer for everyone involved.

Challenges and Limitations of Haptic Feedback Technology
While haptic feedback technology in VR offers exciting possibilities, it also faces several challenges. One major limitation is the complexity of accurately simulating touch sensations. Creating a realistic tactile experience that mimics various surfaces and interactions requires advanced hardware and intricate programming.
Another concern is user comfort. Some users may find certain devices bulky or uncomfortable during extended use. This discomfort can detract from the immersive nature of virtual environments, making it essential for developers to prioritize ergonomics.
Moreover, cost remains a barrier for widespread adoption. High-quality haptic devices often come with hefty price tags, limiting access for many potential users.
Latency issues can also hinder performance. Delays between user actions and corresponding feedback can disrupt immersion and realism in VR experiences. Improving response times continues to be an area needing attention as technology evolves.
The Future of Haptic Feedback in VR
Emerging technologies are on the verge of transforming haptic feedback in VR. As we move towards more immersive virtual environments, advancements will likely enhance tactile sensations.
Imagine feeling the texture of a stone wall or the warmth of sunlight through your hands. Such experiences aren’t far off. Developers are experimenting with advanced materials and sensors that mimic real-life interactions.
Integration with AI could lead to adaptive feedback systems tailored to each user’s preferences. This would create unique touch experiences based on individual reactions.
Moreover, as devices become lighter and more portable, users can enjoy seamless interaction without being tethered to bulky equipment. The focus is shifting toward making these sensations not just realistic but also emotionally resonant.
As research continues, collaborations between tech companies and designers will open doors for innovative applications across gaming, training simulations, and even therapeutic uses in mental health care. The future looks promising for haptic technology in VR spaces.
How to Incorporate Haptic Feedback into Your VR Experience
To enhance your VR experience with haptic feedback, start by selecting the right hardware. Controllers equipped with advanced vibration motors can simulate realistic touch sensations. Consider devices like gloves or vests that provide more immersive interaction.
Next, choose applications designed to utilize haptic technology effectively. Many games and simulations now incorporate tactile responses to actions such as grabbing or touching objects in virtual environments.
Experiment with settings within your VR software. Adjust sensitivity levels for a more personalized feel—too much intensity can be overwhelming, while too little may not convey realism.
Don’t hesitate to participate in communities focused on VR development. Sharing insights about incorporating haptic feedback will help refine techniques and discover new methods that others have successfully implemented.
Keep an eye out for updates in both hardware and software that offer improvements in haptic technology. The field is evolving rapidly, leading to even richer experiences ahead.

Conclusion
The integration of haptic feedback in VR environments marks a significant leap forward in how we interact with virtual worlds. This technology adds a new layer of realism and immersion, transforming passive observation into active participation.
As developers continue to refine their techniques, users can expect even more nuanced sensations that mimic real-life touch. From the gentle caress of wind to the jarring impact of an explosion, each interaction becomes richer and more engaging.
While there are challenges ahead—like cost and technological limitations—the potential for improvements is vast. The future holds exciting possibilities where haptic feedback could redefine gaming, training simulations, therapy sessions, and social interactions within virtual spaces.
Embracing this innovation not only enhances user experiences but also opens doors to creative applications we’ve yet to imagine. For anyone looking to deepen their engagement with VR technologies, exploring ways to incorporate haptic feedback will undoubtedly be rewarding.