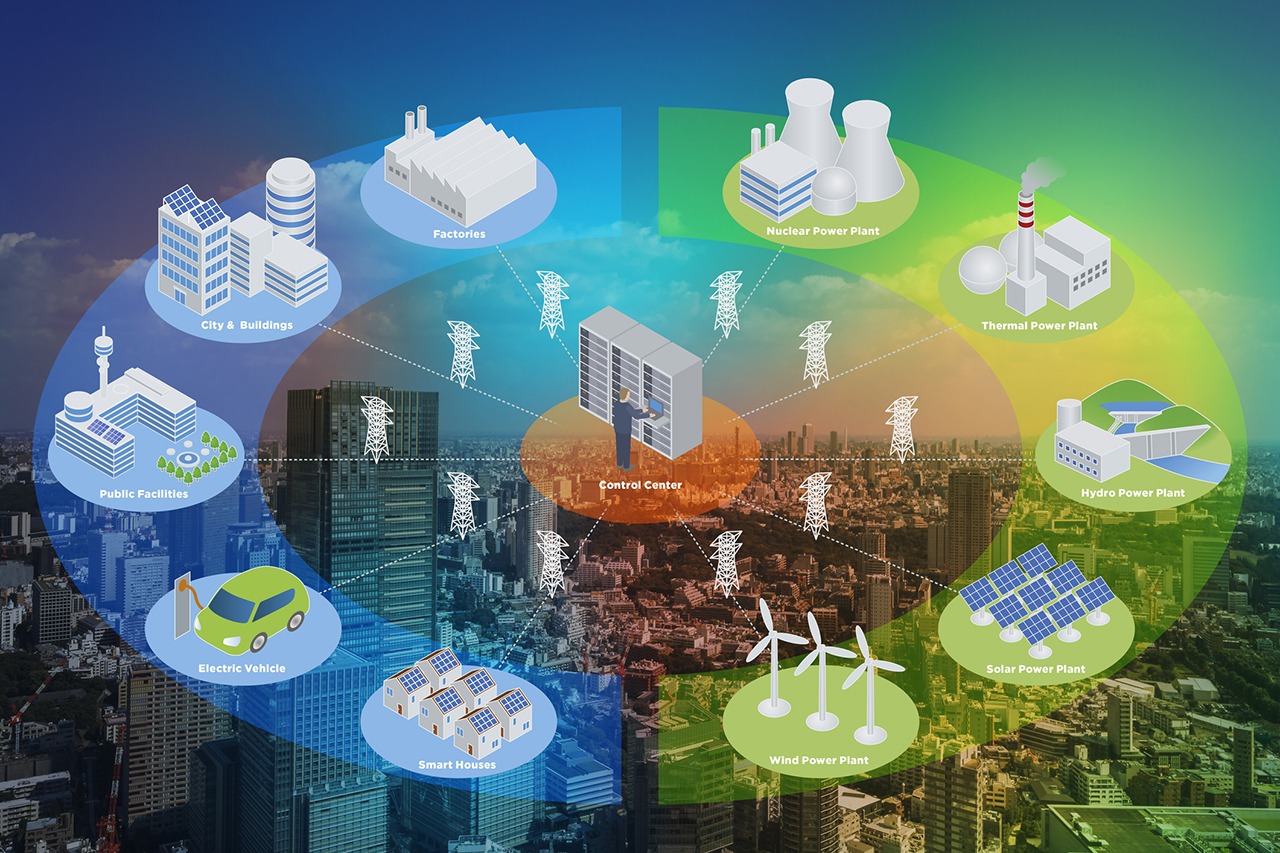
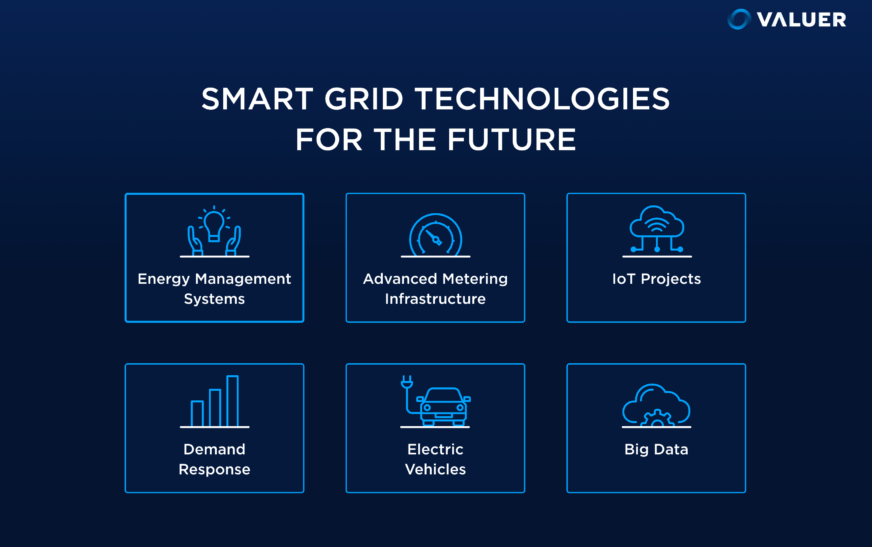
Introduction to Smart Grids
Imagine a world where energy flows seamlessly, where every appliance and device communicates with the grid to optimize power use. Welcome to the era of smart grids—an innovative leap in energy management that promises efficiency, sustainability, and reliability. As our global population grows and technology advances, traditional energy systems struggle to keep pace. Enter smart grids: a comprehensive solution that transforms how we generate, distribute, and consume electricity.
With their ability to integrate renewable resources and respond dynamically to demand fluctuations, smart grids are set to revolutionize not just our homes but entire cities. They hold the key to managing energy consumption intelligently while minimizing environmental impact. Understanding this new frontier is crucial as we navigate toward a more sustainable future in energy management. Let’s explore what makes these advanced networks so vital for tomorrow’s energy landscape.

How Smart Grids Work
Smart grids operate by integrating modern technology with traditional energy distribution systems. They use digital communication tools to monitor and manage the flow of electricity in real time.
Sensors placed throughout the grid collect data on energy usage, demand, and supply. This information is sent to a central system for analysis. By understanding these patterns, utilities can optimize energy distribution.
Advanced software algorithms predict potential outages or spikes in usage. This proactive approach allows for adjustments before problems arise.
Additionally, smart meters installed in homes give consumers insights into their own energy consumption. Users can make informed decisions about when to use power based on pricing signals from the grid.
The result? A more efficient and reliable network that enhances overall performance while reducing waste. The seamless connectivity between all components ensures a dynamic response to changing conditions across the system.
Benefits of Smart Grids
Smart grids revolutionize energy management by enhancing efficiency. They optimize electricity distribution, reducing waste and ensuring that power reaches consumers more reliably.
These advanced systems enable real-time data collection. Utilities can monitor usage patterns and adjust supply accordingly. This leads to fewer outages and faster response times during peak demand.
Cost savings are another significant advantage. Smart grids minimize the need for excess infrastructure while allowing for better load balancing. Consumers often enjoy lower energy bills as a result.
Moreover, they promote sustainability. By integrating renewable energy sources like solar and wind, smart grids support cleaner alternatives to fossil fuels.
They empower users through increased control over their consumption habits. Homeowners can manage their appliances based on pricing signals, leading to smarter choices in daily usage.
Challenges and Solutions
Transitioning to smart grids presents several challenges. One significant hurdle is the substantial investment required for infrastructure upgrades. Traditional systems often lack the technological foundation needed to integrate advanced features.
Cybersecurity also poses a risk. As networks grow more interconnected, they become vulnerable to cyberattacks that can disrupt energy supply and compromise sensitive data.
Additionally, public acceptance of new technologies can be slow. Many consumers are hesitant about change, fearing higher costs or privacy issues associated with smart meters and data collection.
However, solutions exist. Governments and private sectors can collaborate on funding initiatives that ease financial burdens on utilities and consumers alike.
Enhancing cybersecurity protocols through regular audits and updates will help protect against threats. Public awareness campaigns can educate communities about the benefits of smart grids, fostering acceptance and enthusiasm for this necessary evolution in energy management.
The Role of Renewable Energy in Smart Grids
Renewable energy plays a crucial role in the evolution of smart grids. By integrating solar panels, wind turbines, and other sustainable sources, these grids enhance energy reliability.
Smart grids can efficiently manage fluctuating energy outputs from renewable sources. They adjust consumption patterns based on real-time data. This capability helps balance supply and demand seamlessly.
Decentralization is another key aspect. With local generation points, communities become less dependent on centralized power plants. This not only increases resilience but also empowers consumers to take charge of their energy use.
Moreover, incorporating renewables reduces carbon footprints significantly. Transitioning to clean energy aligns with global sustainability goals while promoting healthier environments.
The synergy between smart grids and renewable technologies paves the way for innovative solutions in energy management. It opens up new possibilities for greener living and smarter consumption habits across various sectors.
Impact on Consumers and the Environment
Smart grids significantly influence both consumers and the environment. For consumers, these systems provide enhanced control over energy usage. Real-time data empowers households to make informed decisions about their consumption patterns.
As a result, people can reduce their electricity bills while minimizing waste. This shift towards efficiency can lead to lower demand during peak hours, easing pressure on the grid.
From an environmental perspective, smart grids facilitate greater integration of renewable energy sources. They enable smoother transitions from fossil fuels, promoting cleaner power generation.
Additionally, by optimizing energy distribution and reducing losses in transmission, smart grids contribute to a significant decrease in greenhouse gas emissions.
This collective impact fosters a sustainable ecosystem where technology supports ecological balance and consumer empowerment alike. Such advancements pave the way for smarter living solutions that benefit everyone involved.
Implementation and Adoption Around the World
Countries worldwide are increasingly investing in smart grids to enhance energy management. Each nation has a unique approach, shaped by its specific needs and resources.
In Europe, countries like Germany and Denmark lead the charge with advanced technologies. Their focus is on integrating renewable sources seamlessly into their existing infrastructure.
Meanwhile, the United States is exploring diverse models. From urban areas prioritizing grid modernization to rural regions adopting microgrids for resilience, innovation thrives across states.
Asia presents a contrasting landscape. China’s rapid adoption of smart grid technology showcases its commitment to sustainability while addressing energy demands efficiently.
Emerging economies also see potential in this transition. Nations like India are rolling out initiatives aimed at improving access and efficiency through modernized systems.
International collaboration plays a crucial role too. Sharing best practices fosters faster advancements and builds global knowledge around smart grids’ implementation challenges and successes.
Future Predictions and Technological Advancements
The future of smart grids holds immense promise, driven by rapid technological advancements. Innovations in artificial intelligence and machine learning will enhance grid management. These technologies can predict energy demand patterns more accurately than ever before.
Blockchain is another game-changer on the horizon. It offers secure transactions for energy trading between consumers and producers, fostering a decentralized energy market. This could empower individuals to become active participants in their own energy consumption.
Moreover, the integration of advanced sensors will enable real-time monitoring of grid performance. This leads to quicker responses to outages or inefficiencies, minimizing downtime and enhancing reliability.
As electric vehicles become mainstream, smart grids will adapt accordingly. They’ll not only manage charging stations but also utilize EV batteries as temporary storage solutions during peak demand periods.
These developments paint a dynamic picture for the future of energy management, ensuring smarter use of resources while promoting sustainability across communities.

Conclusion
The evolution of energy management is at the forefront of technological advancements. Smart grids represent a pivotal shift in how we generate, distribute, and consume energy. They promise to enhance efficiency, reliability, and sustainability in our energy systems.
As more countries embrace smart grid technology, the impact on consumers and the environment can be significant. The integration of renewable sources not only reduces carbon footprints but also fosters economic growth through job creation in new sectors.
Looking ahead, it’s clear that the future of energy management lies within these intelligent networks. Continued innovation will lead to smarter solutions that adapt to changing demands while prioritizing environmental health.
Embracing this change requires collaboration among governments, industries, and communities worldwide. As smart grids become increasingly common across global landscapes, their potential remains limitless—transforming our approach to energy for generations to come.