Quantum Supremacy: Achieving problems
Imagine a world where problems that stump classical computers for decades are solved in mere minutes. This is not science fiction; this is the promise of quantum supremacy. As we stand on the brink of a technological revolution, understanding what quantum computing entails becomes increasingly crucial. The concept of achieving supremacy over traditional computing methods opens up new avenues for innovation and discovery across various fields. Whether it’s drug discovery or cryptography, the potential applications seem boundless. Join us as we explore the fascinating journey toward quantum supremacy and unravel how it could reshape our future in ways we’ve only begun to imagine.

Understanding Quantum Supremacy
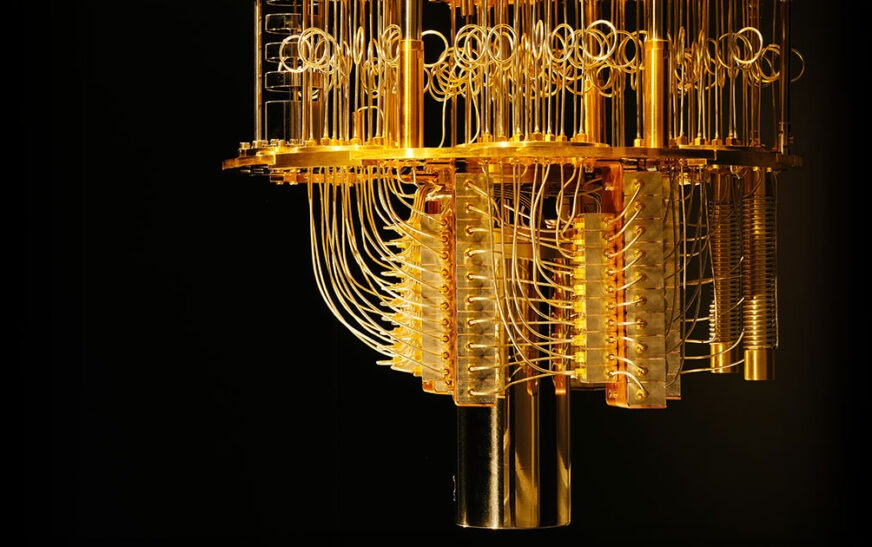
Quantum supremacy refers to a point where quantum computers outperform classical computers in solving specific problems. This milestone signifies more than just speed; it represents an entirely new paradigm of computation.
At its core, quantum computing leverages the principles of quantum mechanics—superposition and entanglement—to process information in ways that were previously thought impossible. Unlike classical bits, which can be either 0 or 1, qubits can exist in multiple states simultaneously. This unique property allows quantum systems to tackle complex calculations at unprecedented speeds.
Understanding this concept requires grasping both its potential and limitations. Quantum supremacy doesn’t imply that every problem will be better solved by a quantum computer; rather, it’s about demonstrating clear advantages for certain tasks over traditional methods. As researchers push boundaries, they unveil possibilities that could revolutionize industries ranging from finance to pharmaceuticals.
History of Quantum Computing
The journey of quantum computing began in the early 1980s. Pioneering physicist Richard Feynman proposed that classical computers could not efficiently simulate quantum systems. This sparked interest and laid the groundwork for a new field.
In 1994, Peter Shor introduced a groundbreaking algorithm capable of factoring large numbers exponentially faster than classical algorithms. His work demonstrated the potential power of quantum machines and ignited further research.
Simultaneously, Lov Grover developed another influential algorithm for searching unsorted databases more effectively using quantum principles. These advancements hinted at a future where complex problems might be solved much quicker than ever thought possible.
As technology evolved, researchers began building prototype quantum computers. Companies like IBM and Google entered the race, investing heavily in developing practical applications for this revolutionary approach to computation. Each milestone brought us closer to realizing true supremacy over traditional methods.
![The History of Quantum Computing You Need to Know [2024]](https://thequantuminsider.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/Capture-6.jpg)
The Race to Achieve Quantum Supremacy
The quest for quantum supremacy has ignited fierce competition among tech giants and research institutions. Companies like Google, IBM, and Rigetti are at the forefront, each vying to be the first to demonstrate that quantum computers can solve problems classical computers cannot.
Google made headlines in 2019 when it announced its achievement of quantum supremacy with Sycamore. They claimed their 53-qubit processor solved a problem in just 200 seconds that would take classical supercomputers thousands of years.
However, skepticism surrounded these claims. Researchers debated whether the specific task showcased real-world applicability or if it was merely a controlled scenario designed for publicity.
IBM quickly countered by demonstrating advancements in error correction and qubit coherence times, underscoring their commitment to practical applications over theoretical milestones. The race extends beyond bragging rights; it’s about unlocking new potentials across industries from cryptography to drug discovery. Each breakthrough promises transformative possibilities we’ve yet to imagine.
How Does Quantum Supremacy Work?
Quantum supremacy occurs when a quantum computer can perform tasks that would be infeasible for classical computers. It leverages the principles of quantum mechanics, particularly superposition and entanglement.
In simple terms, superposition allows quantum bits, or qubits, to exist in multiple states at once. This capability vastly expands computational potential compared to binary bits used in traditional computing.
Entanglement further enhances this power. When qubits become entangled, the state of one instantly influences another, regardless of distance. This interconnected behavior enables complex problem-solving processes far beyond what classical machines can achieve.
When researchers create algorithms designed specifically for these unique capabilities, they unlock solutions to problems like optimization and simulation that were previously unsolvable or required impractical timeframes on conventional systems. The synergy between qubits’ properties is where the magic happens—ushering us into uncharted technological territories with endless possibilities.
Benefits and Applications of Quantum Supremacy
Quantum supremacy opens doors to groundbreaking advancements across various fields. With its ability to process complex calculations at unprecedented speeds, it can tackle problems that classical computers struggle with.
One significant application lies in drug discovery. Quantum systems can simulate molecular interactions, accelerating the search for new medications and treatments.
Financial modeling also stands to benefit greatly. Quantum algorithms could analyze vast datasets quickly, allowing firms to optimize portfolios and manage risks more effectively.
Additionally, quantum computing enhances cryptography. Its capability to break traditional encryption methods leads to the development of stronger security protocols, safeguarding sensitive information.
Industries like logistics may see improvements too. Complex routing problems can be solved efficiently, leading to reduced costs and better resource management.
These potentials illustrate how achieving quantum supremacy is not just a technological milestone but a gateway to revolutionary applications that reshape numerous sectors.

Controversies Surrounding Quantum Supremacy
Quantum supremacy has sparked significant debate within the scientific community. Critics argue that claims of achieving this milestone often overlook practical implications. They question whether we truly understand the full potential or limitations of quantum computers.
Another point of contention is reproducibility. Some researchers assert that results from experiments claiming quantum supremacy may not be easily replicated. This raises concerns about transparency and reliability in reporting breakthroughs.
The environmental impact also garners attention. Quantum computing requires immense resources, including energy-intensive cooling systems for qubits. The sustainability of such operations can’t be ignored as technology evolves.
Moreover, there’s a looming fear regarding security threats posed by powerful quantum algorithms capable of breaking current encryption methods. This adds an ethical dimension to discussions surrounding advancements in quantum technologies.
These controversies highlight the complexities and uncertainties inherent in navigating the frontier of quantum computing.
Future of Quantum Computing and Supremacy
The future of quantum computing is as vast and unpredictable as the universe itself. As researchers push boundaries, we can envision a world where quantum systems address problems long deemed unsolvable by classical computers.
New algorithms are emerging, unlocking potential efficiencies in sectors like drug discovery, logistics optimization, and artificial intelligence. Each advancement brings us closer to harnessing the true power of qubits.
Moreover, collaboration among tech giants and startups is fueling innovation. With increased funding and interest in quantum research, breakthroughs could come at an unprecedented pace.
However, challenges remain. Error correction and qubit stability must improve for practical applications to flourish. The path may be fraught with hurdles but the rewards promise transformative impacts across industries.
As this technology matures, it will redefine computation’s landscape—creating opportunities that were once only imagined in science fiction narratives.
Conclusion
Quantum supremacy represents a pivotal moment in the evolution of computing technology. As researchers and engineers push the boundaries, we’re witnessing a shift from classical computers to quantum processors capable of solving problems previously deemed insurmountable. The historical context reveals how far we’ve come, driven by intense competition among tech giants and academia alike.
Understanding how quantum supremacy works is crucial for grasping its implications on various industries. With applications ranging from cryptography to drug discovery, the potential benefits are vast. However, controversies surrounding the achievements raise questions about reproducibility and practical utility that cannot be ignored.
Looking ahead, the future of quantum computing holds both promise and uncertainty. As we delve deeper into this realm, continued advancements will shape our technological landscape profoundly. It’s an exciting time filled with possibilities as we stand at the threshold of a new era in problem-solving capabilities—one that challenges everything we know about computation today.