Welcome to the dawn of a new era in manufacturing. The landscape is rapidly evolving, and at the heart of this transformation lies Industry 4.0. Imagine machines that communicate seamlessly, data flowing effortlessly between systems, and production lines that adapt on-the-fly to meet changing demands. This isn’t just a vision for the future; it’s happening right now.
As businesses strive to stay competitive in an ever-changing market, smart manufacturing has emerged as a game-changer. It’s about harnessing cutting-edge technologies to create more efficient processes, reduce costs, and enhance quality. But what does it take to embrace this revolution?
Join us as we dive into what Industry 4.0 entails and explore its key technologies, benefits, real-life applications, challenges faced by companies adopting these innovations—and how your business can prepare for what’s next in this exciting journey toward smarter manufacturing solutions.
What is Industry 4.0?
Industry 4.0 represents the fourth industrial revolution, marked by a fusion of advanced technologies reshaping how products are manufactured. This phase emphasizes automation and data exchange in manufacturing environments.
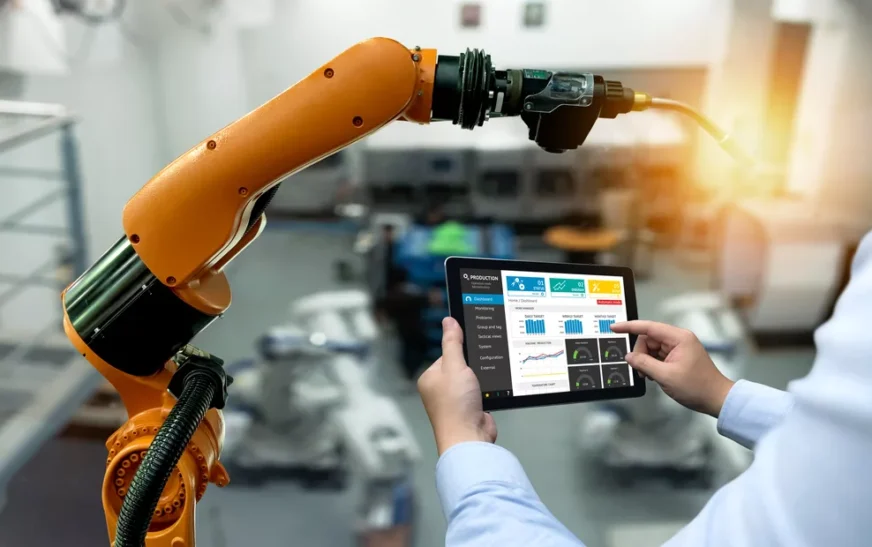
At its core, Industry 4.0 integrates cyber-physical systems, the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, and artificial intelligence. These elements work together to create smart factories where machines can communicate with each other and respond dynamically to real-time data.
This transformation leads to enhanced productivity and efficiency as processes become more streamlined. The ability for machines to learn from their environment allows businesses to predict failures before they occur, reducing downtime significantly.
Moreover, Industry 4.0 encourages customization at scale—enabling companies to meet individual customer needs without sacrificing efficiency or quality. As this revolution unfolds, it opens doors for innovation that was once thought impossible in traditional manufacturing settings.
Key Technologies of Industry 4.0
Key technologies are the backbone of Industry 4.0, driving innovation and efficiency in smart manufacturing.
The Internet of Things (IoT) connects machines, sensors, and devices to create a seamless flow of information. This connectivity allows for real-time monitoring and data analysis.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) plays a crucial role by enabling predictive maintenance and optimizing production processes. With machine learning algorithms, systems can adapt quickly to changing conditions.
Robotics also enhances productivity through automation. Advanced robots perform complex tasks with precision while working alongside human operators.
Another significant technology is big data analytics. It transforms vast amounts of data into actionable insights that inform decision-making processes.
Blockchain technology ensures secure transactions and traceability across supply chains. This transparency boosts trust among all stakeholders involved in manufacturing operations.
Benefits of Implementing Smart Manufacturing in Businesses
Implementing smart manufacturing transforms traditional production processes into streamlined operations. This shift leads to enhanced efficiency and productivity, often resulting in significant cost savings.
Real-time data analysis allows businesses to make informed decisions quickly. With insights gathered from connected devices, manufacturers can anticipate issues before they escalate.
Flexibility is another key advantage. Smart systems adapt easily to changing demands, allowing for customized production without extensive downtime.
Moreover, improved quality control becomes a reality. Automated monitoring detects defects instantly, ensuring that products meet stringent standards consistently.
Employee safety also benefits significantly from automation and smart technologies. Reducing human involvement in hazardous tasks minimizes workplace accidents.
Embracing smart manufacturing fosters innovation within the organization. Companies become agile players in a competitive landscape by leveraging advanced technologies and methodologies.
Real-life Examples of Industry 4.0 in Action
Siemens is a prime example of Industry 4.0 in action. The company integrates digital twins into its manufacturing processes, allowing for real-time simulations that enhance efficiency and reduce waste.
Another innovator is General Electric. They utilize predictive maintenance through IoT sensors, which monitor equipment health and performance. This proactive approach minimizes downtime while maximizing productivity.
In the automotive sector, BMW employs smart factories with automated guided vehicles (AGVs). These AGVs transport materials between production lines seamlessly, ensuring a streamlined workflow without human intervention.
Furthermore, Coca-Cola leverages data analytics to optimize their supply chain operations. With AI-driven insights, they can predict demand trends and adjust production accordingly.
These examples highlight how diverse industries are embracing Industry 4.0 technologies to drive innovation and improve operational effectiveness across the board.

Challenges and Limitations of Smart Manufacturing
Smart manufacturing offers immense potential, but it’s not without hurdles. One major challenge is the high initial investment required for advanced technologies. Many businesses struggle to allocate resources for new systems.
Data security also looms large. As factories become increasingly connected, they face greater risks of cyber-attacks. Protecting sensitive information and infrastructure must be a top priority.
Another limitation lies in workforce readiness. Employees may need extensive training to adapt to new tools and processes, leading to temporary disruptions in production.
Interoperability can complicate matters further. Integrating legacy systems with cutting-edge solutions often proves difficult, hindering seamless communication between devices.
Regulatory compliance poses challenges as industries navigate evolving standards related to technology adoption and data use. This complexity can stall progress towards fully realizing smart manufacturing’s benefits.
Preparing for the Future: How to Adopt Industry 4.0 in Your Business
To adopt Industry 4.0, start by assessing your current processes. Identify areas that can benefit from automation and data analytics. Understanding where you stand is crucial for effective transformation.
Next, invest in training your workforce. Upskilling employees ensures they are ready to embrace new technologies. A knowledgeable team is vital for successful implementation.
Consider starting small with pilot projects. Test systems on a limited scale before full rollout. This approach minimizes risk while allowing you to gauge effectiveness.
Collaboration is key; partner with technology providers who specialize in smart manufacturing solutions. Their expertise can guide you through the complexities of this transition.
Foster a culture of innovation within your organization. Encourage experimentation and open dialogue about new ideas and improvements as this mindset will drive growth into the future.

Conclusion
The landscape of smart manufacturing is rapidly changing with the advancements introduced by Industry 4.0. Businesses that embrace these innovations are not only enhancing their operational efficiency but also positioning themselves for future growth and competitiveness.
Understanding what Industry 4.0 entails is crucial for any business looking to thrive in this new era. The core technologies driving this transformation—IoT, AI, robotics, and big data analytics—offer unprecedented opportunities for optimization and innovation.
Implementing smart manufacturing comes with a myriad of benefits. Companies can expect increased productivity, improved product quality, enhanced flexibility in production processes, and reduced operational costs. These advantages make a compelling case for businesses to transition towards smarter systems.
Real-life examples illustrate the tangible impact of Industry 4.0 initiatives across sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods. Companies are already experiencing significant gains from adopting advanced manufacturing practices that leverage connected devices and intelligent algorithms.
However, challenges remain on the path toward fully realizing smart manufacturing potential. Issues like cybersecurity threats, high initial investment costs, workforce retraining needs, and integration complexities cannot be overlooked.
To prepare effectively for the future of smart manufacturing within your organization requires strategic planning and commitment to continuous learning about emerging technologies in industry action today.
Navigating these waters may seem daunting at first blush but staying informed will keep you ahead of competitors while unlocking new possibilities along the way.






